
Introduction to Connectivity Evolution
The Emergence of 4G and LTE Networks
As we moved into the age where the internet became as essential as electricity, a quantum leap in mobile connectivity was inevitable. This leap materialized with the emergence of 4G and LTE networks. Around the same time, these technologies began to define the modern standards for communication. Their introduction marked a dramatic enhancement in the speed and quality of wireless communication. Whether it’s streaming high-definition videos, enjoying mobile gaming, or managing IoT devices, 4G vs LTE networks have set the scene for today’s mobile data revolution.
Finding the Meaning: Understanding 4G and LTE
Grasping the true significance of 4G vs LTE requires diving into what each term embodies. “4G” stands for the fourth generation of wireless technology, following its predecessor 3G. This generation was designed to provide more bandwidth and higher data rates, allowing for richer multimedia experiences and faster response times. On the other hand, LTE, which means “Long-Term Evolution,” is a standard for wireless broadband communication. It’s a specific type of 4G that focuses on enhancing network capacity and speed.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a subtle distinction. True 4G, as defined by standards organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), requires certain speed thresholds that LTE doesn’t always meet. Nevertheless, LTE is sometimes referred to as “4G LTE” because it represents a significant step toward those 4G speeds and offers a noticeably faster experience compared to 3G networks. It’s this powerful combination that has significantly transformed our interaction with mobile devices, allowing for a smoother and more responsive user experience.
Comparing 4G and LTE
Speed and Performance
4G and LTE networks have revolutionized mobile connectivity, offering faster speeds than 3G and significantly enhancing user experiences. While 4G was initially envisioned with ambitious speed targets set by the ITU-R, LTE networks typically provide download speeds ranging from 50 to 150 Mbps, with advanced standards like LTE-Advanced potentially doubling or tripling these rates. Despite falling short of the original 4G benchmarks, LTE still represents a substantial leap forward from 3G. This improved speed and performance enable almost instantaneous access to data, smooth streaming of HD content, and faster downloads and uploads, benefiting both consumers and businesses relying on real-time data transfer. The table below provides a concise comparison of the key aspects of LTE and 4G networks.
|
Aspect |
4G |
LTE |
|
Speed |
Lower maximum download and upload speeds compared to LTE, typically ranging from 5 to 50 Mbps for downloads and 2 to 20 Mbps for uploads. |
Significantly faster download and upload speeds, typically ranging from 5 to 100 Mbps for downloads and 2 to 50 Mbps for uploads. |
|
Latency |
Slightly higher latency compared to LTE, which may slightly impact real-time interactive experiences. |
Generally lower latency, resulting in faster response times for interactive applications like online gaming and video calling. |
|
Efficiency |
Less efficient spectrum utilization compared to LTE, which may struggle to support as many simultaneous users or provide consistent speeds in congested areas. |
More efficient spectrum utilization, allowing for greater capacity and supporting more simultaneous users without sacrificing speed or performance. |
Coverage and Availability
4G and LTE networks offer extensive coverage, especially in developed regions, gradually replacing older 3G networks. LTE, a type of 4G technology, has a broad presence, particularly in urban areas, although not all “4G” areas provide full LTE speeds. Coverage varies based on factors like location, network infrastructure, and carrier capacity. Carriers continually upgrade networks, providing tools like coverage check apps for users to anticipate service availability. It’s crucial to verify coverage maps before selecting a carrier. As 5G networks emerge, efforts are made to ensure they complement existing 4G LTE services rather than replace them entirely.
Compatibility and Device Support
Compatibility and device support are essential for maximizing the benefits of 4G vs LTE networks. Most modern smartphones and tablets are equipped with 4G LTE capabilities, ensuring broad support for these networks globally. However, device compatibility with specific carrier frequency bands can be a challenge. Each carrier operates on different frequency bands, and not all devices support all bands. It’s crucial to ensure your device supports your carrier’s frequency bands for the best experience. Purchasing unlocked devices with broad band support or verifying compatibility before committing to a device or network is advisable. Manufacturers are also prioritizing future-proofing devices to be compatible with emerging network standards. This cross-compatibility is crucial for seamless user experiences and avoiding connectivity issues.
Limitations and Challenges
While 4G and LTE have advanced mobile connectivity, they face challenges. Network speeds can vary due to factors like congestion and infrastructure limitations. Maintaining consistent speeds across coverage areas requires significant investment. Spectrum availability is also a concern, with higher frequencies offering faster speeds but shorter ranges. The growing number of connected devices can strain networks, leading to degraded service. Operators and manufacturers are addressing these challenges to prepare for future demands, including the integration of 5G technologies.

Quality and Data Consumption
Analyzing Signal Strength and Stability
Signal strength and stability are paramount for ensuring a seamless and reliable mobile experience in today’s interconnected world. The quality of your connection hinges upon the strength of the signal your device receives, typically measured in decibel milliwatts (dBm). While an LTE signal strength reading around -80 dBm is considered excellent, real-world scenarios often present a range of readings, with signals around -90 dBm to -100 dBm being more common. In this context, understanding the intricacies of signal strength and stability becomes crucial for troubleshooting connectivity issues and selecting the most reliable service provider and mobile devices. Let’s delve into the factors affecting signal quality, the importance of stability, and potential remedies for enhancing signal strength, ensuring you maximize the benefits of strong and stable 4G and LTE connections.
- Critical Importance: Signal strength and stability are paramount for a reliable mobile experience, influencing connection quality and performance.
- Measurement Parameters: Various parameters like RSSI, RSRP, RSRQ, and SINR are used to assess signal quality in wireless networks, with RSRP being specific to LTE networks.
- Signal Strength: An LTE signal strength around -80 dBm is considered excellent, but real-world scenarios often yield readings between -90 dBm to -100 dBm.
- Impact of Low Signal Strength: Habitually low signal strength can result in slower internet speeds, dropped calls, and an unreliable connection.
- Signal Stability: Stability is as crucial as strength, ensuring consistent connection speeds and reduced latency. Fluctuating signals can cause intermittent connectivity issues.
- Factors Affecting Signal: Distance from cell towers, building materials, and geographical features like hills influence signal strength and stability.
- Remedies for Weak Signals: Solutions include using signal boosters, relocating to areas with better coverage, and selecting mobile devices with advanced antennas and signal processing capabilities.
- Continuous Network Enhancement: Mobile carriers improve signal strength and stability by adding cell sites and employing advanced technologies.
4G vs. LTE Data Usage: What Costs More?
When it comes to data usage, the difference in costs between 4G vs LTE networks isn’t significant. The amount of data consumed primarily depends on the content being accessed rather than the network technology. Activities like streaming video, browsing, gaming, or downloading have fixed data footprints across different network types. However, faster speeds with 4G may lead users to consume more content in the same time frame compared to LTE. This could include simultaneous activities like streaming music, downloading files, and browsing social media feeds.
Costs for 4G services aren’t necessarily higher than LTE. Pricing depends on carrier plans, which may bundle data allowances with other features. Additionally, high-definition content can consume more data and potentially increase costs. Carriers offer various plans with tiered data limits or unlimited options, which impact overall costs. Monitoring data consumption and selecting a plan aligned with usage habits are crucial for managing costs effectively on either network. In summary, it’s not 4G versus LTE in terms of data costs; it’s about how you use your data and the plan you choose. Staying within data limits or selecting an unlimited plan can help manage costs while enjoying high-speed connectivity.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Impact on Industries and Everyday Life
The advent of 4G and LTE has transformed industries, enhancing operations and service delivery. In healthcare, telemedicine thrives with HD video consultations connecting patients and specialists worldwide. Retail enjoys faster transactions and improved online shopping experiences, ensuring customer engagement with swift load times and seamless navigation.
- Telecommunications: Enhanced data speeds and reliability have expanded services like video streaming and IoT connectivity.
- E-commerce: Faster mobile internet drives increased online shopping via smartphones.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring benefit from real-time connectivity.
- Transportation: Improved logistics and vehicle tracking streamline operations.
- Media and Entertainment: Streaming services thrive with uninterrupted high-speed internet.
- Manufacturing: Industrial automation flourishes with real-time monitoring and control.
Everyday life is profoundly impacted by 4G vs LTE. Tasks like streaming movies and video conferencing, once tethered to wired connections, are now portable. Social media and communication apps are more dynamic, supporting high-res live streaming and instant multimedia sharing. Additionally, smart homes and cities flourish, relying on fast, reliable data transmission for connected devices to operate seamlessly.
- Communication: High-quality voice/video calls and messaging are ubiquitous.
- Information Access: Instant access to news, education, and resources empowers learning.
- Navigation: Navigation apps provide real-time updates and directions.
- Entertainment: Streaming and gaming on mobile devices are popular pastimes.
- Productivity: Remote work thrives with mobile collaboration tools.
As these technologies continue to develop, their impact is poised to become even more transformative, altering the very fabric of how we live, work, and play on a daily basis.
The VoLTE Advantage: Voice Calls Over LTE Networks
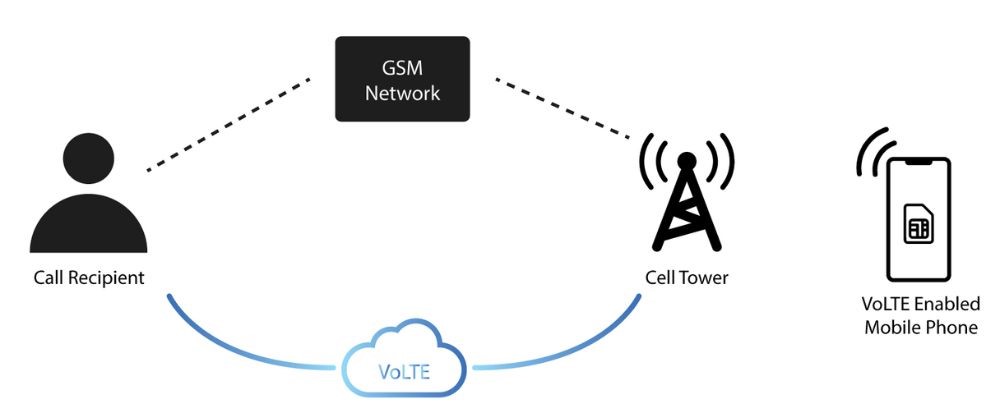
Voice over LTE (VoLTE) provides several advantages for users on LTE networks. It allows voice calls to be transmitted as data over LTE, resulting in clearer, higher-quality calls compared to traditional cellular networks. With VoLTE, users experience improved call quality with HD Voice, offering crisp clarity due to a broader spectrum of audio frequencies. Another benefit of VoLTE is the ability to use voice and data simultaneously without compromising quality, unlike some 3G networks where voice calls interrupt data services. Users can browse the internet, use GPS, or stream content at LTE speeds while on a call.
VoLTE calls also connect more rapidly than traditional cell calls, reducing the time between dialing a number and call connection, thus improving usability and communication efficiency. Most carriers offer VoLTE calls without consuming data from the user’s plan. Instead, they are billed per minute or included in unlimited call packages, aligning with current plan norms. However, VoLTE requires both carrier and device support. Its widespread adoption is prompting the phase-out of older 2G and 3G networks, encouraging consumers and manufacturers to adopt VoLTE-compatible devices.
In summary, VoLTE offers superior call quality, improved connectivity, and efficient use of the data network. As carriers expand VoLTE coverage and more devices become VoLTE-ready, users can expect a more reliable, high-quality service leveraging LTE’s robust capabilities.
Future-Proofing Your Devices: Compatibility Concerns
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, future-proofing mobile devices is crucial to avoid rapid obsolescence. This involves assessing compatibility with emerging network technologies like 5G while maintaining functionality within current 4G vs LTE frameworks. To future-proof a device:
- Consider Compatibility: Look for devices supporting a broad range of frequency bands and latest wireless technology standards to adapt to carrier updates and new spectrum allocations.
- Assess Software Support: Evaluate the manufacturer’s track record for providing software updates, which extend device viability by improving features, security, and network compatibility.
- Dual SIM and eSIM Support: Consider devices with dual SIM and eSIM technology for flexibility in switching carriers or service plans without physical SIM card changes, adapting to the best network available.
Future-proofing isn’t about remaining cutting-edge indefinitely but about choosing devices with robust hardware, software support, and versatility. This ensures devices remain assets rather than limitations during transitions from 4G and LTE to 5G and beyond.

FAQs on 4G and LTE
Will My Current Device Support Both 4G vs LTE?
To determine if your device supports both 4G and LTE, check its technical specifications, usually found in the ‘Settings’ menu or manufacturer documentation. Most modern smartphones and tablets, including those labeled as 4G LTE, support both technologies. Ensure your device’s supported frequency bands align with your carrier’s for optimal performance. Here are the steps to check 4G/LTE compatibility on your phone:
- Open Settings: Go to your phone’s settings menu.
- Find About Phone: Look for “About Phone” or “About Device.”
- Navigate to Network Settings: Access network or connectivity settings.
- Check Supported Networks: Look for “LTE” or “4G” among the supported network types.
- Verify Frequency Bands: Ensure supported frequency bands match your carrier’s for 4G/LTE.
- Refer to Documentation: If needed, consult manufacturer documentation or search online for detailed compatibility information.
If your device doesn’t support 4G LTE or you want compatibility with future network technologies, consider upgrading to a newer model with broader compatibility.
Is There a Significant Cost Difference Between 4G and LTE Services?
When comparing the costs of 4G and LTE services, it’s important to note that carriers typically price their plans based on data usage rather than the specific network technology. Since both 4G and LTE are part of the same mobile generation, providers usually don’t differentiate between them in pricing structures. Your plan’s cost is determined by your data consumption rate, such as streaming or browsing, rather than the network type.
However, because 4G often offers faster speeds than standard LTE, you might use up your data more quickly, potentially leading to higher costs if you exceed your monthly limit or need to upgrade to a larger data plan. To avoid unexpected charges, monitor your data usage and choose a plan that suits your needs, whether it’s a set data limit or an unlimited plan.
Carriers offer various options, including promotional deals or bundling services, which can provide additional value. Ultimately, selecting a plan that matches your usage habits ensures you effectively manage expenses while enjoying the benefits of fast and reliable 4G or LTE connections.
Can 4G and LTE Coexist with Emerging 5G Networks?
Yes, 4G and LTE can and do coexist with emerging 5G networks, playing a pivotal role in the transition to the next-generation wireless technology. This coexistence is an intentional design of the mobile network evolution strategy, where 5G networks are built upon existing 4G LTE infrastructure. This intentional strategy, known as non-standalone 5G (NSA 5G), utilizes existing LTE infrastructure while introducing newer technologies. Devices maintain connectivity to both 5G and LTE, ensuring continuous service, even in areas with limited 5G coverage. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) optimizes spectrum use, allowing efficient operation of both technologies across various frequencies. LTE’s widespread coverage and device support make it essential in complementing and supporting the deployment of 5G networks.
AirVoice Wireless utilizes both 4G/LTE and 5G+ networks, prioritizing the fastest connection available in your area. This approach ensures users experience seamless connectivity and coverage all over the United States while benefiting from the advancements of both technologies.




Leave A Comment